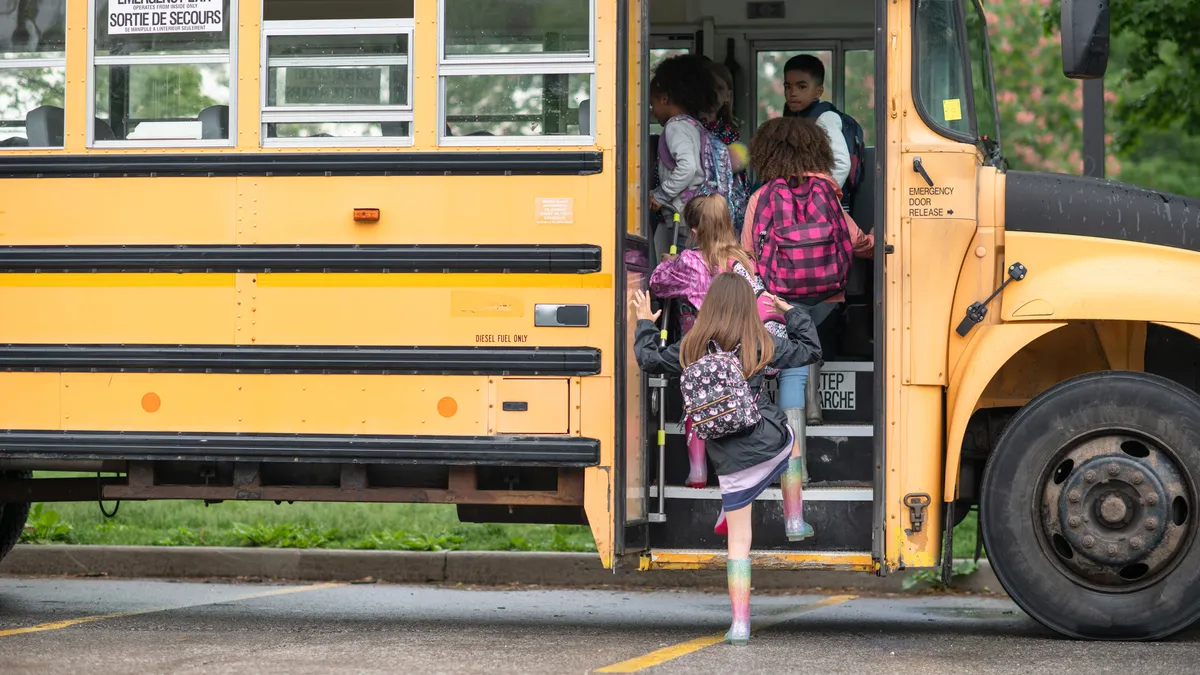Public school student enrollment across the U.S. dipped slightly by 0.3% to 49.3 million in the 2024-25 school year compared to the year before, according to data released in December by the U.S. Department of Education for the 50 states and the District of Columbia.
Meanwhile, the number of operating elementary and secondary public schools decreased by 0.2% — from 99,297 in 2023-24 to 99,073 in 2024-25.
The data release, part of the Education Department's annual Common Core of Data collection, does not offer explanations for the trends, but it does mirror reported enrollment dips that are leading some school systems to consider school closures or consolidations.
Although many factors may contribute to each community's school enrollment figures, nationally, some experts have said lower birthrates and increased school choice competition are having an adverse impact on public school enrollment.
On the other hand, some states are seeing year-over-year enrollment increases, including the District of Columbia (2%) and Arkansas (1.2%), according to an analysis of the federal data by Burbio, a business intelligence service that works with suppliers to K-12 education. The three states that lost the most students between the 2023-24 and 2024-25 school years were Louisiana (5.9%), Maine (3.5%), and West Virginia (1.9%).
Here are some other figures from the Education Department and from the Burbio's analysis:


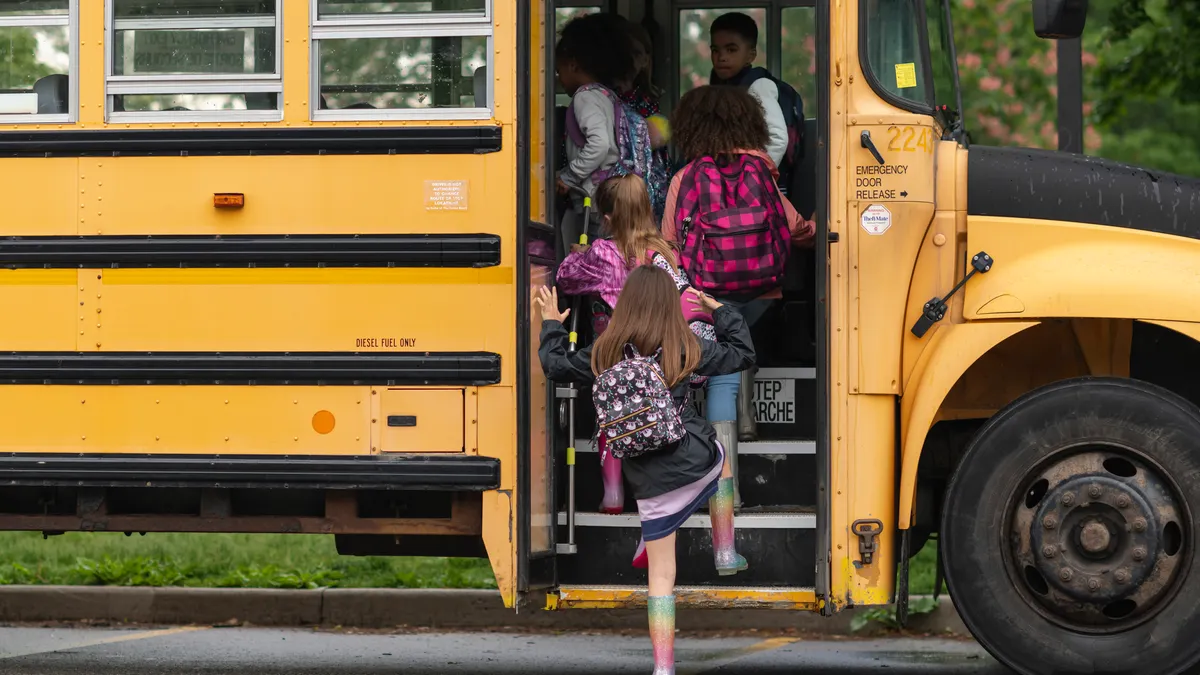




 Dive Awards
Dive Awards